
Historical Background of Iran-China Economic Partnership

Historical Context of Iran-China Trade Relations
The trade relationship between Iran and China transcends recent developments, boasting a rich history that dates back to antiquity.
- Ancient Silk Road: Historically, the Silk Road facilitated numerous exchanges between the Persian Empire and ancient China, establishing early trade links.
- Modern Era Resurgence: Contemporary ties began to strengthen significantly in the 1980s after the Iran-Iraq war, with China emerging as one of Iran’s major trading partners.
- Strategic Partnerships: The turn of the 21st century saw the two nations enhancing their economic partnership, bolstered by strategic investments, particularly in energy and infrastructure.

Economic Significance of the Iran-China Partnership
Iran’s strategic location and China's economic prowess make their partnership pivotal.
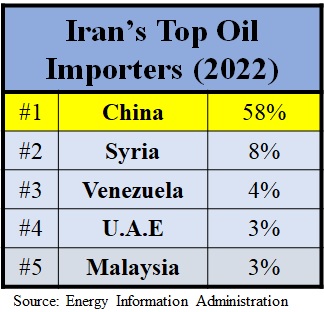
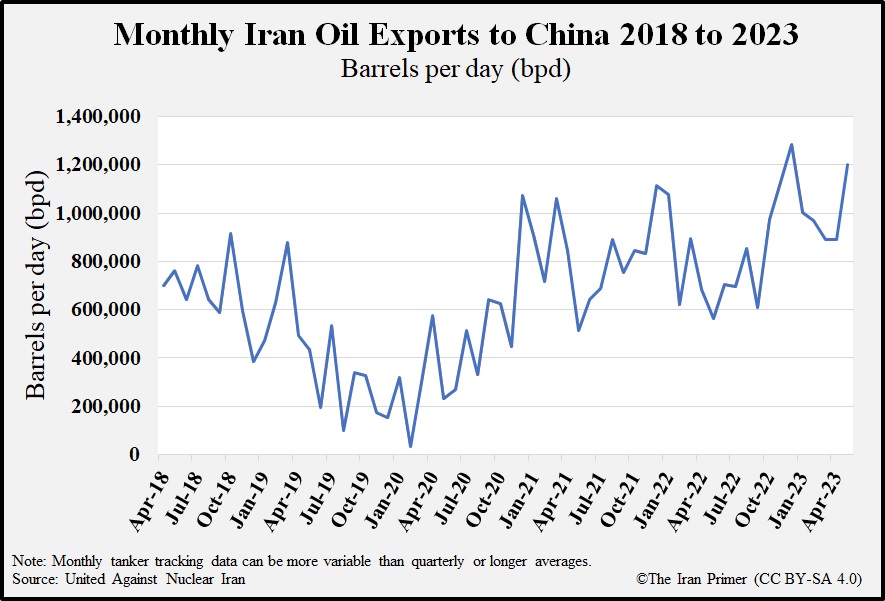
- Energy Trade: Iran is a major supplier of crude oil to China, fulfilling a substantial part of China’s energy needs.
- Infrastructure and Development: Chinese investments, particularly in Iran's energy infrastructure and transportation projects, drive Iran’s economic growth.
- Regional Influence: This partnership enhances China’s economic influence in the Middle East, counterbalancing the impacts of the China-US trade war and contributing to economic stability in the region.

Key Agreements and Investments

Overview of Major Agreements Between Iran and China
A range of significant agreements anchor the Iran-China economic partnership.
- 25-Year Comprehensive Cooperation Agreement: Signed in March 2021, this ambitious pact aims to deepen bilateral ties, covering areas like energy, infrastructure, industrial capacity, and cultural exchanges.
- Oil and Gas Contracts: Multiple contracts have been inked, with China investing in Iran's oil fields and refineries to secure steady energy supplies.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Iran's inclusion in the BRI underscores its strategic importance, leading to investments in Iranian railways and ports, enhancing connectivity and trade routes.

Significant Investment Projects in Iran by Chinese Companies
Chinese investments are crucial for Iran's economic development. Significant projects include:
- Oil and Gas Sector: China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) has heavily invested in the South Pars gas field, one of the world's largest.
- Transportation: China has funded the Tehran-Mashhad high-speed railway project, improving Iran's internal connectivity.
- Port Development: Investments in Chabahar Port under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) aim to enhance Iran’s trade capacity, providing a critical link to Central Asia.
These projects underscore the strategic depth and mutual benefits of the Iran-China partnership.
Impact on Global Trade
Effects of Iran-China Economic Partnership on Global Trade Dynamics
The Iran-China economic partnership significantly alters global trade dynamics.
- Energy Diversification: China's imports of Iranian oil challenge traditional dominance by Western energy markets, influencing global oil prices.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Iran’s strategic position in the BRI enhances trade connectivity between Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, reshaping international trade routes.
- Geopolitical Shifts: The partnership stabilizes regional economies, diminishing reliance on Western trade alliances and countering the effects of the China-US trade war by boosting China's economic resilience through diversified trade partnerships.

Implications for Regional Economic Stability and Cooperation
The Iran-China economic partnership has profound implications for regional stability and cooperation.
- Economic Resilience: Chinese investments bolster Iran's economy amid Western sanctions, ensuring economic resilience and growth.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Infrastructure projects like the Tehran-Mashhad railway and Chabahar Port augment regional connectivity, facilitating smoother trade and cooperation among neighboring countries.
- Regional Influence: By integrating Iran into major economic initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), the partnership promotes regional economic cohesion, which is crucial for stability and mitigating the impacts of regional tensions and crises.

Criticisms and Challenges

Challenges Faced by the Iran-China Economic Partnership
Despite its potential, the Iran-China economic partnership encounters several challenges.
- Sanctions Pressure: U.S. and EU sanctions on Iran complicate financial transactions and investments, limiting the full potential of bilateral trade.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Regional conflicts and political instability pose risks to ongoing and future projects, threatening economic stability.
- Logistical Hurdles: Implementing large-scale infrastructure projects involves significant logistical challenges, including regulatory hurdles and coordination issues, which can delay progress.
These factors necessitate strategic planning and resilience to sustain and grow the partnership effectively.

Criticism from International Organizations and Countries
The Iran-China economic partnership faces criticism from various international quarters.
- Western Governments: The United States and European Union criticize the partnership for undermining sanctions aimed at curbing Iran's nuclear ambitions, challenging global diplomatic efforts.
- Regional Concerns: Neighboring countries express apprehension about China's growing influence in Iran, fearing a shift in regional power dynamics.
- NGOs and Human Rights Groups: Criticisms also stem from issues related to labor practices and environmental concerns associated with large-scale Chinese investments in Iran.
These critiques underscore the complexity and geopolitical ramifications of the partnership, necessitating diplomatic navigation.
Future Prospects and Opportunities

Potential Growth Areas in Iran-China Economic Cooperation
Several sectors highlight potential growth in Iran-China economic cooperation.
- Renewable Energy: Investment in solar, wind, and hydroelectric projects can meet Iran's sustainable energy goals, diversifying energy sources beyond oil and gas.
- Technology Transfer: Collaborations in technology and innovation, including telecommunications and AI, can enhance Iran's technological infrastructure.
- Agriculture: Supporting Iran's agricultural sector through modern farming techniques and investment ensures food security and boosts exports.
In these areas, cooperation can foster economic prosperity, leveraging mutual strengths for sustainable development. Options for growth present opportunities to deepen bilateral ties further effectively.

Opportunities for Mutual Benefit and Sustainable Development
The Iran-China partnership offers numerous opportunities for mutual benefit and sustainable development.
- Infrastructure Development: Continued Chinese investment in Iran's transportation and energy infrastructure propels economic growth, creating jobs and enhancing trade routes.
- Resource Sharing: Iran’s rich natural resources complement China’s industrial demand, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials and energy.
- Cultural Exchange: Boosting educational and cultural exchanges fosters deeper mutual understanding and cooperation, laying the groundwork for long-term diplomatic and economic ties.
These collaborative efforts pave the way for durable economic prosperity and sustainable development, benefiting both nations strategically and economically.

Conclusion

Assessment of the Game-Changing Potential of the Iran-China Economic Partnership
The Iran-China economic partnership holds transformative potential for both nations and beyond.
- Economic Diversification: For Iran, diversifying away from Western-dominated markets reduces economic vulnerability, enhancing stability.
- Strategic Influence: China’s investment in Iran boosts its geopolitical leverage in the Middle East, a region critical for global energy and trade routes.
- Global Trade: This alliance reshapes global trade dynamics, challenging established economic powers and forging new pathways under initiatives like the Belt and Road.
By altering traditional power balances and trade routes, this partnership has the potential to be a significant game-changer in global economics.

Key Takeaways and Implications for the Future of Global Trade Relations
The Iran-China partnership has critical implications for global trade. Key takeaways include:
- Shift in Power Dynamics: Strengthened Iran-China ties challenge Western economic hegemony, particularly the US and EU.
- Trade Route Diversification: Enhanced connectivity through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) redefines traditional trade routes, increasing Asia's influence in global trade.
- Geopolitical Realignment: The partnership may prompt other nations to reassess their trade policies and alliances, fostering a more multipolar world economy.
These factors underscore the transformative potential of the Iran-China alliance on future global trade relationships.