
Background on UN Warning of Regional Insecurity in West Africa

Overview of the Recent Developments in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger
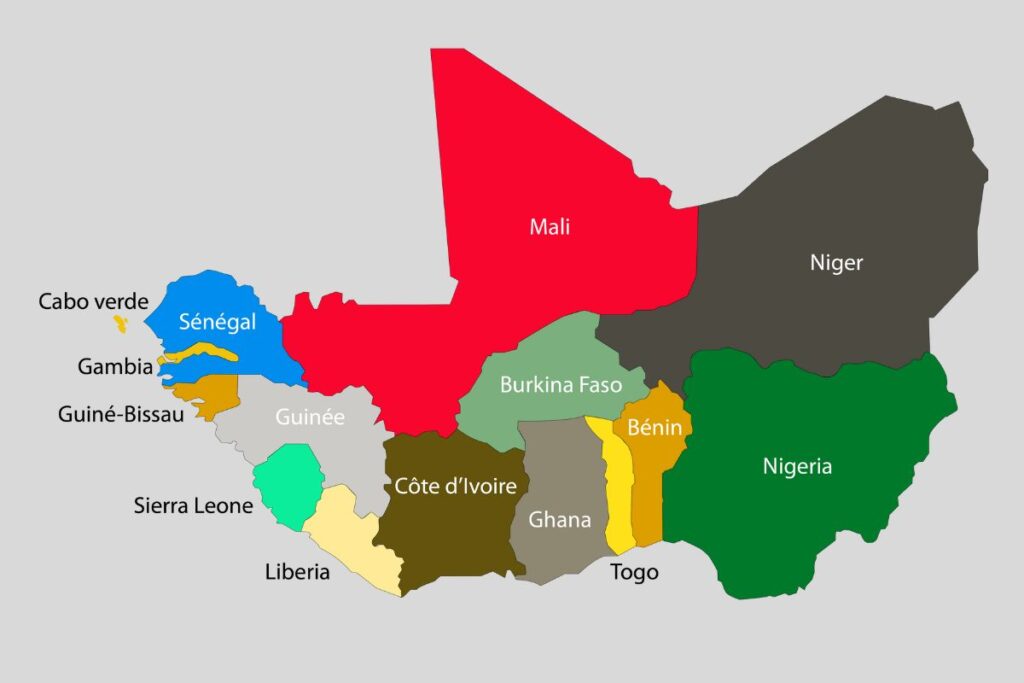
The recent shifts in the political and security landscape of West Africa, particularly in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger, have garnered widespread attention. These nations have made significant and impactful decisions that are reshaping regional dynamics.
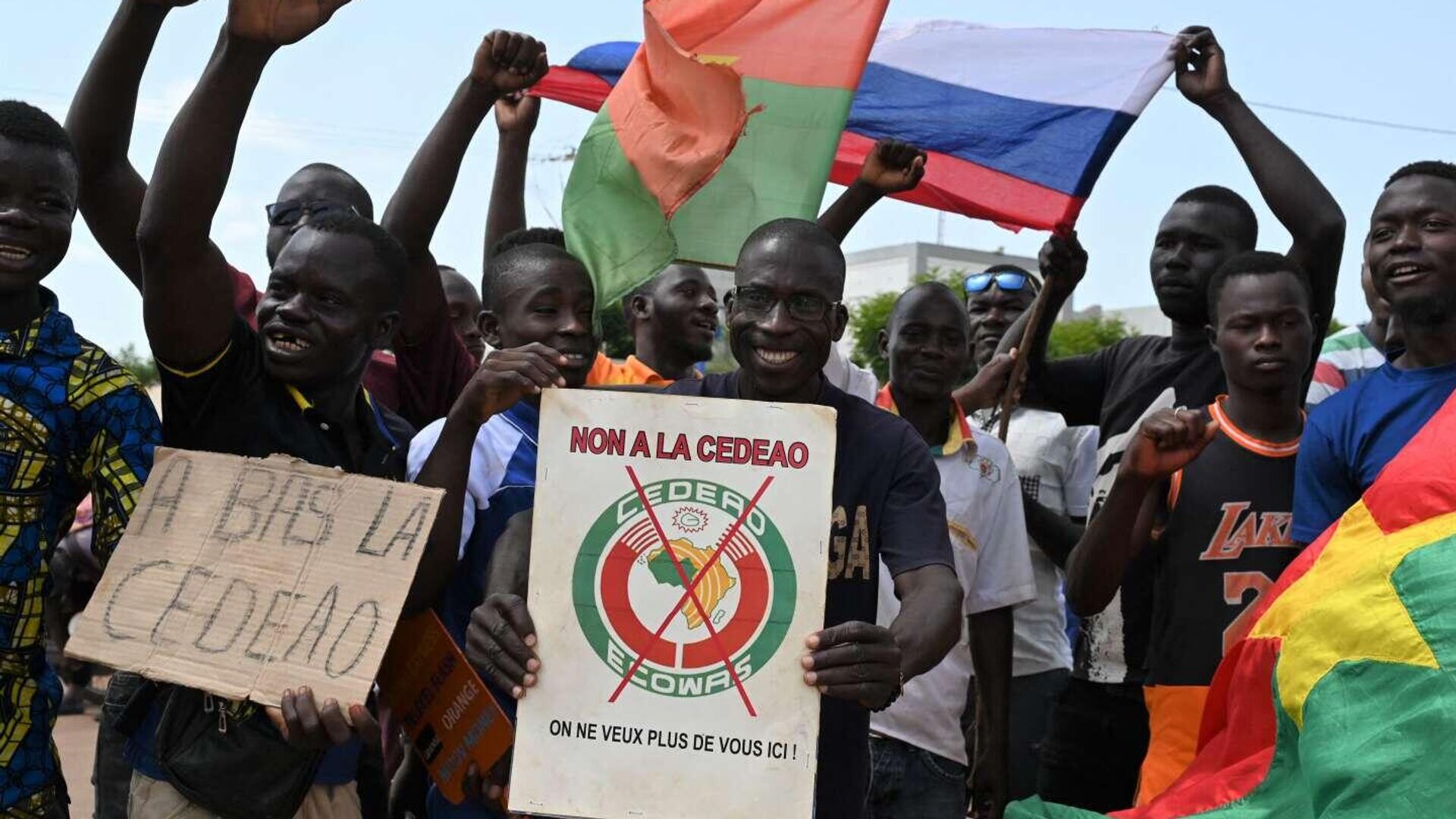
Mali: - Political Instability: Mali has experienced several coups and persistent political turmoil. - Withdrawal from ECOWAS: Triggered by dissatisfaction over external influence and security concerns.
Burkina Faso: - Rising Insurgencies: The nation faces increased terrorist activities, destabilizing central governance. - ECOWAS Exit: Motivated by perceived inefficacies in regional support and security.
Niger: - Security Challenges: Niger's struggle with border security and militant threats. - ECOWAS Withdrawal: Decision driven by geopolitical and internal security considerations.
These developments have left a significant imprint on West Africa's political and security fabric, prompting serious deliberations on the future of regional cooperation.
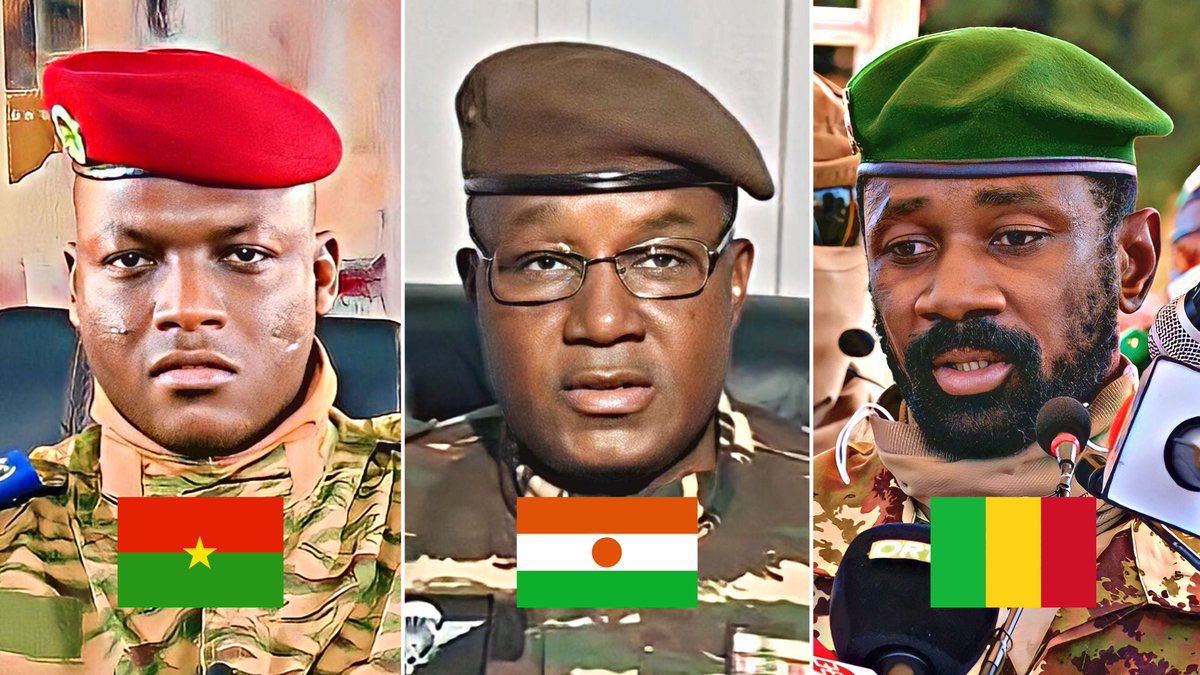

Analysis of the Implications of ECOWAS Withdrawals
The recent decisions by Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger to withdraw from the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) signal profound implications for the region. These withdrawals pose significant challenges to both regional and international efforts to maintain stability.
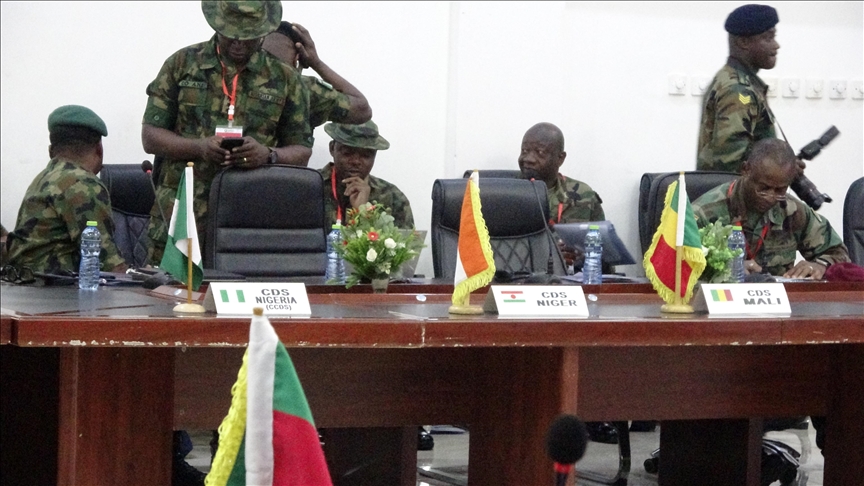
Impact on Regional Security: - Fragmented Security Efforts: Hindered unified response to terrorism and insurgency. - Weakening of Collective Defense: Loss of coordinated military and intelligence operations.
Economic Consequences: - Trade Disruptions: Negative effects on intra-regional trade and economic growth. - Investment Concerns: Diminished confidence from international investors and partners.
Political Ramifications: - Weakened Political Leverage: Reduced capacity to influence regional policies and governance. - Increased Vulnerability: Nations become more susceptible to external manipulations and internal unrest.
These implications highlight the urgent need for renewed strategies and collaborations to address the emergent challenges in West Africa.

Mali's Withdrawal from ECOWAS

Reasons Behind Mali's Decision to Withdraw from ECOWAS
Mali’s withdrawal from ECOWAS represents a critical juncture in its relationship with the regional bloc. This decision stemmed from multiple complex factors that have been brewing for years.
Political Discontent: - Repeated Coups: Political instability undermining confidence in regional integration. - Governmental Frustration: Perception of insufficient support from ECOWAS in addressing internal crises.
Security Concerns: - Unrelenting Insurgencies: Persistent terrorist activities overwhelming national resources. - Ineffective ECOWAS Measures: Dissatisfaction with ECOWAS’s security interventions and strategies.
Economic Constraints: - Sanctions and Economic Pressure: Negative economic fallout from ECOWAS-imposed sanctions. - Desire for Autonomy: Aiming to regain economic control and tailor policies more closely to national interests.
These reasons underscore the deep-seated issues that have influenced Mali's pivotal decision to exit ECOWAS, complicating the regional security and political framework.

Impact of Mali's Withdrawal on Regional Stability
Mali's withdrawal from ECOWAS has far-reaching effects on regional stability, creating ripples across West Africa's socio-political and security landscape.
Security Dynamics: - Weakened Collective Security: Mali’s exit undermines coordinated regional efforts to combat terrorism. - Increased Terrorist Activities: Potential spike in terrorist attacks exploiting the fragmented security framework.
Political Fragmentation: - Loss of Influence: Reduced collective bargaining power in regional and international political arenas. - Shifting Alliances: Possible re-alignment of political partnerships and alliances within the region.
Economic Ramifications: - Trade Barriers: Disruption in trade flows and economic activities within the ECOWAS trading bloc. - Investor Sentiment: Decreased investor confidence, leading to potential withdrawal of international investments.
These impacts highlight the immediate and long-term challenges posed to West African stability and underscore the need for innovative solutions and strategic collaborations.

Burkina Faso's Withdrawal from ECOWAS

Factors Contributing to Burkina Faso's Exit from ECOWAS
Following Mali’s departure, Burkina Faso's exit from ECOWAS further exacerbates regional instability. Multiple underlying factors influenced this pivotal decision.
Security Challenges: - Rising Insurgencies: Escalating terrorist and militant activities destabilizing the country. - Dissatisfaction with ECOWAS Response: Perceived inadequacies in regional security strategies and interventions.
Political Motivations: - Internal Political Turmoil: Coups and political instability driving a desire for greater autonomy. - National Sovereignty: A push to reclaim control over national security and political frameworks.
Economic Strains: - Economic Sanctions: Severe impacts from ECOWAS sanctions leading to economic hardships. - Economic Independence: Drive to implement tailored economic policies without regional constraints.
These factors illustrate the complexities behind Burkina Faso's exit and emphasize the significance of addressing the root causes to foster regional cohesion and stability.
Consequences of Burkina Faso's Withdrawal on Regional Security
Burkina Faso's decision to leave ECOWAS adds another layer of complexity to the regional security landscape. The move has several immediate and potentially long-term consequences.
Increased Vulnerability: - Gaps in Defense Coordination: Loss of a unified front, making the region more susceptible to terrorist attacks. - Isolated Efforts: Burkina Faso's withdrawal leaves it handling security threats solo, straining national resources.
Destabilization: - Ripple Effect: Potential for other countries to consider similar exits, further weakening regional security alliances. - Migration and Refugee Crisis: Increased cross-border movement due to heightened insecurity affecting neighboring countries.
Economic Impact: - Security Funding: Shifts in funding allocations from regional projects to national defense efforts. - Humanitarian Concerns: Strain on humanitarian aid and development programs, exacerbating regional crises.
These consequences emphasize the urgent need for rethinking and reinforcing regional security strategies to counteract the destabilizing effects of Burkina Faso's withdrawal.

Niger's Withdrawal from ECOWAS

Motives for Niger's Departure from ECOWAS
Niger's decision to depart from ECOWAS adds another dimension to the evolving political and security dynamics in West Africa. Several critical factors have driven this significant move.
Security Considerations: - Border Insecurity: Persistent threats from militant groups and cross-border insurgencies. - Insufficient Regional Support: Perception that ECOWAS has not adequately addressed Niger’s unique security challenges.
Political Factors: - National Sovereignty: Desire to regain complete political autonomy and decision-making power. - Governmental Discontent: Frustration over regional policies perceived as misaligned with Niger’s national interests.
Economic Motivations: - Economic Sanctions: Adverse effects of ECOWAS-imposed sanctions prompting an economic reassessment. - Tailored Economic Policies: Need for economic strategies better suited to Niger’s specific context and needs.
These motives highlight the intricate interplay of security, political, and economic factors that led to Niger's departure, signaling the complexity of ensuring cohesive regional cooperation.

Effects of Niger's Withdrawal on Regional Cooperation and Peace
Niger's withdrawal from ECOWAS introduces significant challenges to regional cooperation and peace efforts, further complicating the West African security and political landscape.
Reduction in Cooperative Efforts: - Weakening Regional Unity: Loss of a key member reduces the strength of collaborative initiatives. - Disjointed Policies: Divergent national policies may replace previously unified regional strategies.
Security Collaboration: - Fragmented Security Tactics: Less cohesive coalition to combat terrorism and insurgency. - Resource Allocation: Shifts in resources from collective security measures to national defense systems.
Peacebuilding and Diplomacy: - Diplomatic Strain: Increased potential for diplomatic conflicts and reduced cross-border cooperation. - Humanitarian Impact: Strained efforts to address humanitarian crises, affecting refugee support and aid distribution.
The effects of Niger's withdrawal underscore the urgent need to revisit and revitalize regional frameworks to maintain cooperation and foster long-term peace in West Africa.

UN Response to Regional Insecurity in West Africa

Actions Taken by the UN to Address the Escalating Insecurity
In response to the growing insecurity in West Africa, precipitated by the withdrawal of Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger from ECOWAS, the United Nations has initiated several crucial actions.
Enhanced Peacekeeping Efforts: - Increased Deployment: Additional UN peacekeeping forces to stabilize volatile regions. - Integrated Missions: Coordination with local governments to ensure effective deployment and operations.
Diplomatic Interventions: - Mediation Efforts: Facilitating dialogues between conflicting parties to foster peaceful resolutions. - Political Support: Aid in establishing robust governance structures to mitigate political instability.
Humanitarian Aid: - Emergency Relief: Provision of essential supplies and services to displaced populations and affected communities. - Development Programs: Long-term initiatives to address root causes of instability, such as poverty and lack of education.
These actions underscore the UN's commitment to restoring stability in West Africa, highlighting the importance of coordinated international efforts in addressing complex security challenges.

Strategies Proposed to Mitigate the Potential Threats in the Region
To combat the escalating insecurity in West Africa, various strategies have been proposed to address and mitigate potential threats.
Strengthening Regional Security: - Enhanced Intelligence Sharing: Promoting collaboration among neighboring countries for better threat detection and response. - Joint Military Operations: Coordinated efforts to conduct joint operations against insurgent and terrorist groups.
Promoting Political Stability: - Supporting Governance Reforms: Encouraging democratic processes and robust governance structures. - Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Establishing regional frameworks to mediate and resolve political disputes effectively.
Economic Development Initiatives: - Investment in Infrastructure: Building critical infrastructure to stimulate economic growth and improve social conditions. - Employment Programs: Creating job opportunities to address unemployment, reducing the appeal of extremist ideologies.
These proposed strategies aim to foster a resilient and stable West Africa by addressing the root causes of instability and reinforcing cooperative regional frameworks.

Conclusion

Assessment of the Collective Impact of ECOWAS Withdrawals
The withdrawal of Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger from ECOWAS has led to multidimensional consequences, collectively reshaping the regional landscape.
Security Consequences: - Increased Instability: Fragmentation of security efforts has led to heightened vulnerability to terrorist activities. - Reduced Coordination: Lack of a unified response complicates joint military operations and intelligence sharing.
Economic Repercussions: - Trade Disruptions: Intra-regional trade has suffered due to diminished economic integration. - Investment Withdrawal: International investors are wary, potentially leading to reduced foreign direct investment.
Political Ramifications: - Weakening Regional Influence: The collective bargaining power of the region is compromised. - Shifts in Alliances: Emergence of new, smaller coalitions potentially altering regional dynamics.
The collective impact underscores the pressing need for renewed regional cooperation and strategic initiatives to navigate the evolving challenges and restore stability in West Africa.
Recommendations for Fostering Peace and Security in West Africa
In light of the collective impact of recent ECOWAS withdrawals, it is crucial to adopt strategic recommendations to foster peace and security in West Africa.
Reinforcing Regional Cooperation: - Re-engagement with ECOWAS: Efforts to reintegrate Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger into ECOWAS to rebuild unified security protocols. - Strengthening Alliances: Forming new partnerships within and beyond the region to enhance collective security and economic stability.
Addressing Root Causes: - Socio-Economic Development: Investing in education, healthcare, and job creation to address the underlying issues fueling instability. - Good Governance Practices: Promoting democratic governance and transparency to strengthen political stability.
Enhanced Security Measures: - Advanced Training: Providing specialized training for national and regional security forces. - Border Security: Implementing robust border management systems to prevent the spread of insurgencies.
By adopting these recommendations, West Africa can significantly improve its prospects for lasting peace and security, thereby facilitating sustainable development and regional cooperation.