The Listeria Outbreak Story Unfolds
Timeline of the Listeria Outbreak
Initial Reports: In January 2023, health officials first identified several cases of listeriosis linked to deli meats. Early Investigations: By February, the CDC began an in-depth investigation, examining supply chains and affected regions. Source Identification: By March, contamination was traced back to a single processing plant, forcing immediate closures. Public Notifications: April saw widespread public alerts and advisories, emphasizing the risks of consuming certain deli meats. Product Recalls: Throughout May, numerous recalls were issued across major retailers. Ongoing Monitoring: By June, increased scrutiny and testing ensured no further spread. This timeline highlights critical moments defining the outbreak's scope.

The Source of Contamination
Identification of the Facility: The contamination source was pinpointed to a well-known deli meat processing plant. Inspection Findings: Inspections revealed lapses in sanitation protocols and equipment maintenance, which facilitated bacterial growth. Affected Products: Several popular deli meat products were identified as tainted, impacting numerous brands. Supply Chain Impact: The intricate supply chains exacerbated the situation, broadening the contamination's reach. Root Cause Analysis: Further analysis determined that inadequate temperature controls and cross-contamination during processing were primary culprits. Preventative Action: The processing plant implemented rigorous new safety measures to prevent future occurrences. This underscores the importance of strict hygiene practices.
Understanding Listeria and Its Dangers

Listeria Bacteria: Characteristics and Risks
Microbial Profile: Listeria monocytogenes is a pathogenic bacterium commonly found in soil, water, and animal feces. Resilience: This bacterium can withstand low temperatures, even thriving in refrigerated environments. Modes of Transmission: Contamination often occurs in processed foods, including dairy products, deli meats, and vegetables. Health Risks: When ingested, Listeria can cause listeriosis, a serious infection particularly dangerous to pregnant women, newborns, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. Symptoms: Listeriosis symptoms include fever, muscle aches, and gastrointestinal issues. Severe cases can lead to meningitis or septicemia. Understanding these characteristics and risks is crucial for effective prevention and control.

Health Impacts of Listeriosis
Initial Symptoms: Listeriosis often begins with mild flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, and muscle aches. Gastrointestinal Distress: Patients frequently experience nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, adding to their discomfort. Vulnerable Populations: Pregnant women face increased risks, often leading to complications such as miscarriage, stillbirth, or premature delivery. Severe Complications: In severe cases, Listeria can spread to the nervous system, causing meningitis or septicemia. Long-Term Effects: Long-term health impacts may include persistent neurological issues in severe cases. These health impacts underscore the importance of early detection and prompt medical treatment.
Response and Remediation Efforts

Industry Recall Actions
Immediate Response: Upon identifying the contamination source, affected companies issued immediate recall notices to remove tainted products from shelves. Scope of Recall: The recalls impacted a broad range of deli meat products across various brands, emphasizing a precautionary approach. Consumer Alerts: Retailers and manufacturers distributed extensive consumer alerts through multiple channels, including social media, press releases, and in-store notices. Logistics: Retailers worked swiftly to retrieve contaminated items, ensuring they were isolated and destroyed safely. Post-Recall Measures: Manufacturers undertook comprehensive reviews of their processes to enhance safety and prevent recurrence. These industry recall actions were critical in mitigating the outbreak's impact and safeguarding public health.
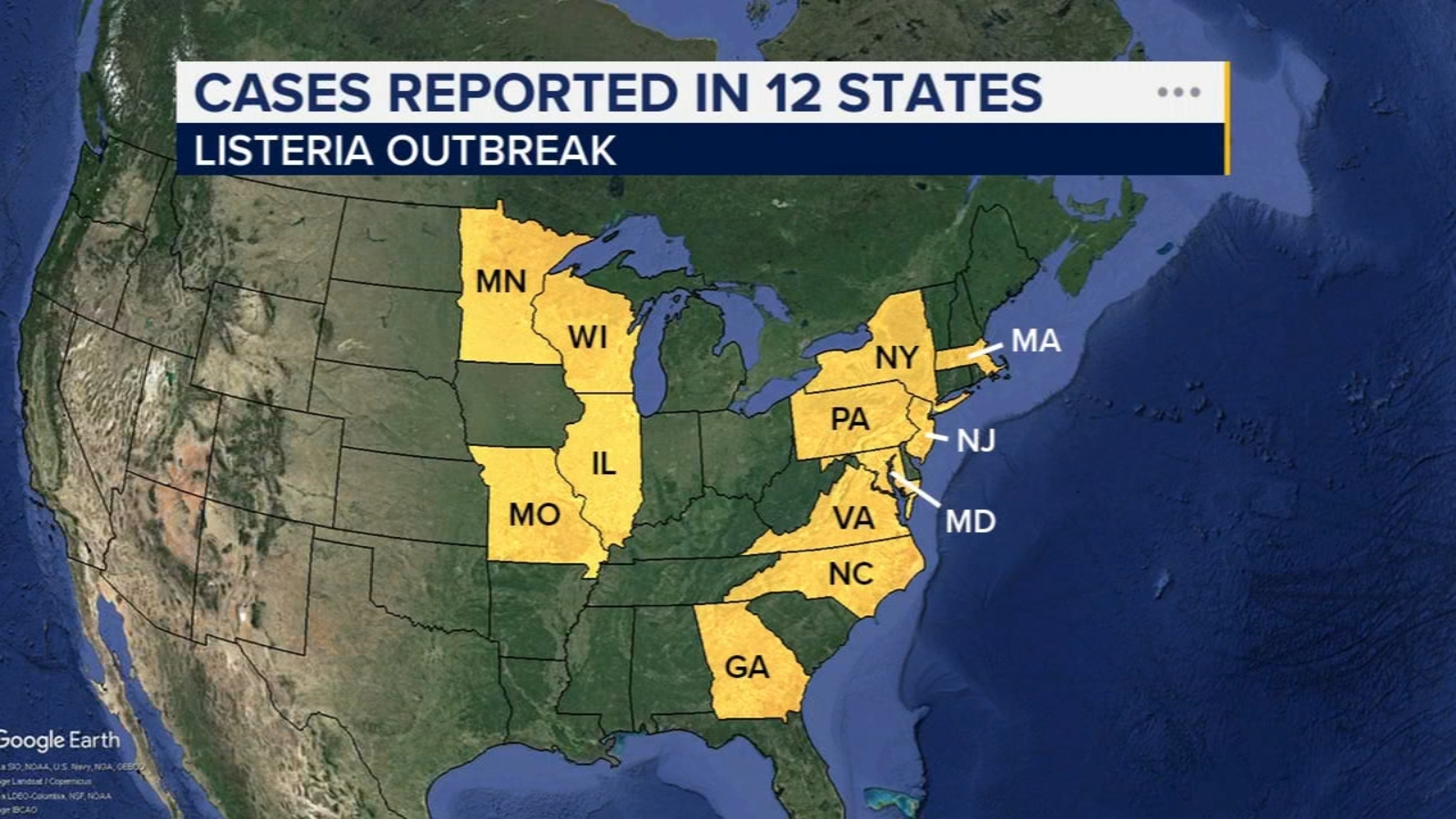
Government Health Measures
Investigative Actions: Government agencies, including the CDC and FDA, launched thorough investigations to identify contamination sources. Public Advisories: Health authorities issued widespread public health advisories, instructing consumers to avoid specific deli meat products. Inspections and Audits: Government inspectors conducted rigorous audits of food processing facilities to ensure compliance with safety standards. Policy Implementation: New policies were introduced to tighten regulations around food processing and handling, aimed at preventing future outbreaks. Educational Campaigns: Authorities also initiated educational campaigns to inform the public about the risks of Listeria and safe food practices. These measures reflect the proactive efforts by government agencies to protect public health and prevent further contamination.
Lessons Learned and Preventative Measures

Food Safety Regulations and Compliance
Regulatory Framework: Food safety is governed by strict regulations, established by agencies like the FDA and USDA, to ensure consumer protection. Compliance Requirements: Food processing facilities are required to adhere to rigorous sanitation and hygiene practices, regularly audited to ensure compliance. Hazard Analysis: HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) protocols are mandatory to identify and mitigate contamination risks at critical stages. Training Programs: Ongoing employee training in food safety practices is essential for maintaining high standards and regulatory compliance. Penalties and Enforcement: Non-compliance can result in substantial penalties, including fines and facility shutdowns. These regulations are designed to uphold the highest food safety standards and prevent incidents like the Listeria outbreak.

Strategies to Avoid Listeria Contamination
Strict Sanitation: Maintaining rigorous cleaning and sanitizing protocols in food processing areas is crucial to eliminate Listeria presence. Temperature Control: Ensuring proper refrigeration and temperature management prevents bacterial growth, particularly in deli meats. Cross-Contamination Prevention: Implementing strict measures to prevent cross-contamination, such as using separate equipment for raw and cooked products, is essential. Regular Testing: Frequent microbial testing of products and surfaces helps in early detection of potential contamination. Employee Training: Continuous training ensures that staff are aware of best practices in hygiene and food safety. Adopting these strategies helps in significantly reducing the risk of Listeria contamination in food products.
Conclusion

Reflections on the Listeria Outbreak
Impact Analysis: The Listeria outbreak from deli meats served as a stark reminder of vulnerabilities within the food safety system. Response Evaluation: The swift recall actions and government measures were commendable, minimizing further health impacts. Lessons Learned: The outbreak highlighted the necessity for stringent food safety protocols and continuous review of practices. Industry Improvements: Significant advancements in monitoring and preventive strategies have been implemented post-outbreak. Consumer Awareness: Increased public awareness about food safety and hygiene practices has been another positive outcome. Reflecting on this outbreak underscores the importance of vigilance, prompt response, and ongoing improvement in food safety standards.

Looking Ahead: Preventing Future Outbreaks
Enhanced Surveillance: Continuous improvements in food safety surveillance systems can detect and address contamination early. Technological Innovations: Adopting advanced technologies such as AI for pattern recognition and real-time monitoring can bolster safety measures. Regulatory Enhancements: Ongoing updates to food safety regulations ensure they keep pace with industry changes and emerging threats. Educational Initiatives: Expanding education programs for both consumers and industry workers promotes safer food handling practices. Collaborative Efforts: Strengthening partnerships among government, industry, and academia can facilitate research and innovative solutions. Focusing on these proactive measures will be crucial to prevent future Listeria outbreaks and safeguard public health.